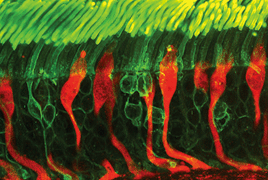
In vivo corneal confocal microscopy (CCM) represents a new, non-invasive, rapidly developing corneal examination technique that enables individual layers of the cornea to be displayed at the cellular level. The cornea is the translucent and at the same time the most innervated tissue of the human body. Diabetic neuropathy (DN) is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus (DM). A close correlation has been demonstrated between the development of diabetic neuropathy and the pathological changes of the corneal subbasal plexus. Currently, great attention is directed towards the possibility of using CCM to determine early DN. Interestingly, changes in nerve plexus in the cornea precede the clinical manifestations of DN. Our work aims to give a comprehensive overview of the current possibilities and trends in use of in vivo CCM in connection with DN evaluation. In vivo CCM becomes important in the search for patients at risk of developing DN, in early diagnosis of DN in pre-symptomatology, in quantifying severe DN, in monitoring and evaluating the therapeutic response to DM treatment. In addition to its diagnostic and preventive significance, it is a research tool important for understanding the pathophysiology of DM changes.
- Uncorrected near visual acuity after monofocal intraocular lens implantation
- Treatment of keratoconus by accelerated cross-linking
- Pars plicata vitrectomy in premature newborns for retinal detachment as a result of retinopathy of prematurity, our results
- Brown's syndrome: The individual forms and their treatment (including expander of own construction)
- In vivo Corneal confocal microscopy: Basic principles and applications
- Possibilities od in vivo corneal confocal microscopy of corneal nerves in diabetes